Session 1.2 Basic Python -1: Variables and Types
2.1 Number and String
1,2,3.. is number
print(1) will print 1
"I am learn Python" is a string
print ("Hi") will print a string in output.
2.1.1 Let Python do math for you
Math is the basic function of the Python, please try below code and learn the basic operation of “+,-,*, /, %”
x = 3
y = 4
answerPlus = x+y
answerMinus = x-y
answerMultiple = x*y
answerDivide = x/y
answerWhatEver = (x*y)+(x-y)/x
answerMode=x%y
print(x) #3
print(y) #4
print(answerPlus) #7
print(answerMinus) #-1
print(answerMultiple) #12
print(answerDivide) #0.75
print(answerWhatEver) #11.666666666666666
print(answerMode) #3
2.1.2 Assign a Number to a Variable and print it
Use print() function you could print the result, but python can’t print mix the data type of number and a string.
Below is working
x = 3
print(x)
But this is not working:
print("x="+x)
You will got error like below:

To correct the type error, you need convert the number to string first.
print("x=" + str(x))
2.1.3 More Assignment example
Assign a expression to a variable
x = 3
y= x+2
example of chain assignment
a = b = x*(y+x)
Check the results:
print("a="+ str(a))
print("b="+ str(b))
please try yourself and print the result.
2.1.4 Math Operators in Python
There are more math operators you may need, pleas try them and see how it works.
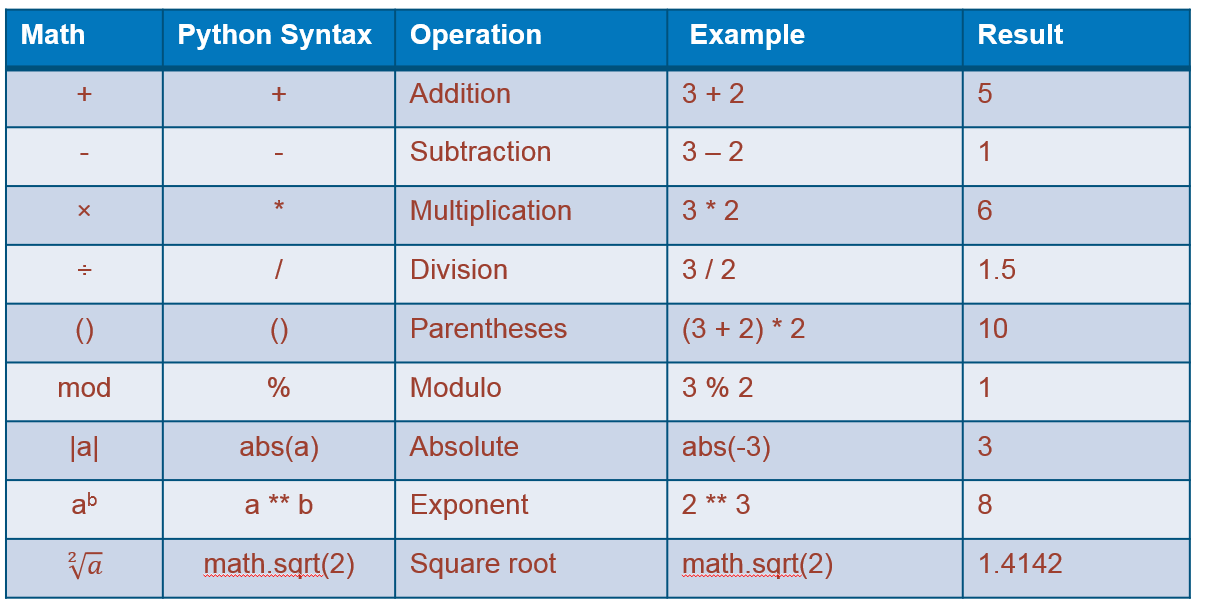
2.1.5 practices
-
use python get the answer of below express 3 + 8 × 9 ÷ 7 × ( 5 +6 )
-
Update your previous turtle drawing project, using some of math to change the graphic pattern
2.2 Type
2.2.1 Type of number: Int and float
All variable has a type in python, for example, the string “abc” has a type “String”.
The number 1,2,3 is integer number, but 1.23 is fraction number.
In python, the integer number type is int the fraction number type is float
You could use type(variable) to get the type of the variable
number = 9
print (type(number))
float_number = 9.0
print(type(float_number))
you will got below type

2.2.2 Convert the number type
The type of number could convert each other:
number = 9
f_number= float(number)
print(number)
print(f_fumber)
please run it ans see the result yourself.
3.2.3 Augmented Assignment
Augmented assignment is the combination, in a single statement, of a binary operation and an assignment statement:
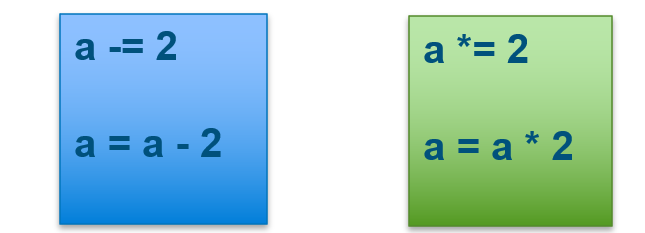
Try below code to see the result
number = 9.0
print("number = " + str(number))
number -= 2
print("number = " + str(number))
number += 5
print("number = " + str(number))
2.3 Boolean Type and Operators
2.3.1 Boolean Type
The Boolean Type only have two value: true and false
You could compare two value and see the result:
- To check if two variable value is same:
a = 2
b = 3
c = 2
result1 = (a == b)
print(result1) # false
result2 = (a == c) # true
print(result2) # true
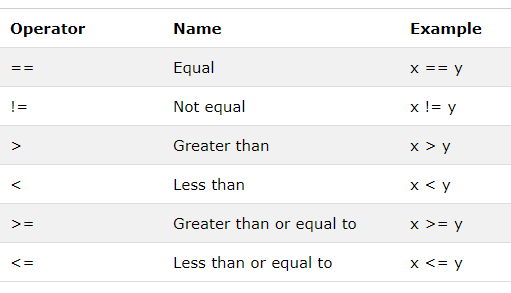
2.3.2 Comparison Operator
There is more operation will got boolean result:
2.3.3 Logic Operators
Logic operators are used to combine the two boolean statements:
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| and | Return true if both are true | x<4 and x>1 |
| or | Return True if one of the value is true | x<4 or x>10 |
| not | reverse the result | not(x>y) |
2.4 Practice
-
Write a Python program, given a radius value, it compute and area of the circle. example: r = 1.1 Area = 3.8013271108436504
-
Please use python print all value between 1 and 10, with the condition:
- x>1 and x<5