06 String & Characters
6.1 Python Strings
A String is a sequence of characters ( or call symbols)

- String “Python String!” is combination of 15 characters or symbols
- Each Characters/symbols was stored in computer as number
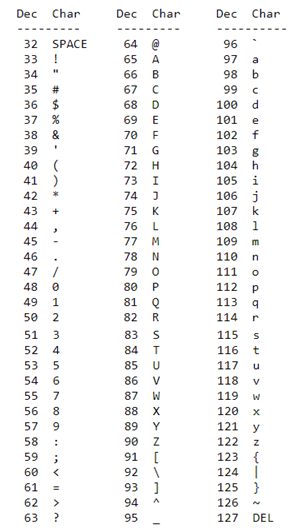
- The most popular numbering system is ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange)
6.1.1 Code to find the ASCII value
The function ord() could convert character to ASCII value.
value_P = ord('P')
print("ASCII value of 'P' is ", value_P)
#Upper case 'P' is 80
value_p = ord('p')
print("ASCII value of 'p' is ", value_p)
#lower case 'p' is 112
The function chr() could return character from the ASCII value.
6.1.2 The ASCII Table
6.1.3 Print ASCII
You could use loop to print ASCII characters
for x in range(20):
t=""
for y in range(20):
t+=(chr(30+x+y))
print(t)

6.1.4 Print String with Color
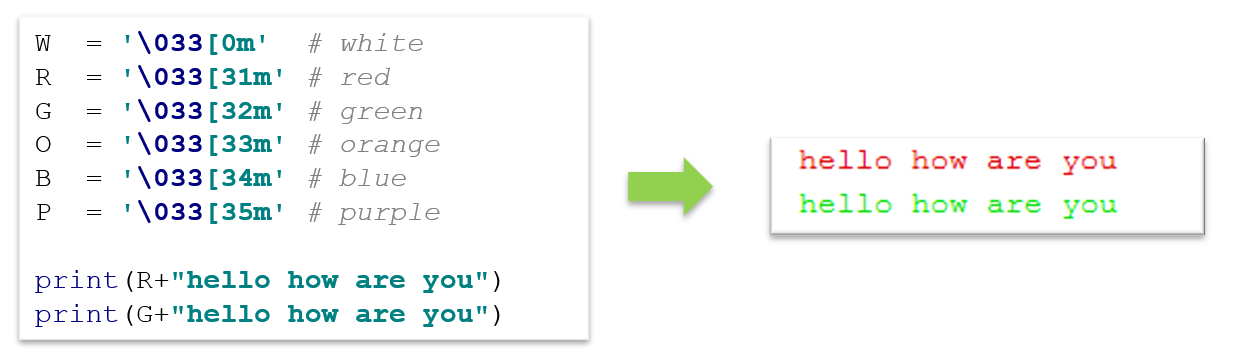
print(R+"hello how are you")
print(G+"hello how are you")
6.1.5 Practice below useful string functions
testStr = "Hello World"
#to upper case
print(testStr.upper())
#to lower case
print(testStr.lower())
# get the length
print(len(testStr))
#insert string to another string
print("*".join(testStr))
# use join to reverse a string
print("".join(reversed(testStr)))
# replace a string
print(testStr.replace("o",chr(210)))
#split a string in to array
print(testStr.split(" "))
6.1.6 DIY, Use Characters to Print ASCII Arts
There is some examples, Please create one yourself



6.2 Cipher: Make a secret string
6.2.1 Caesar Cipher


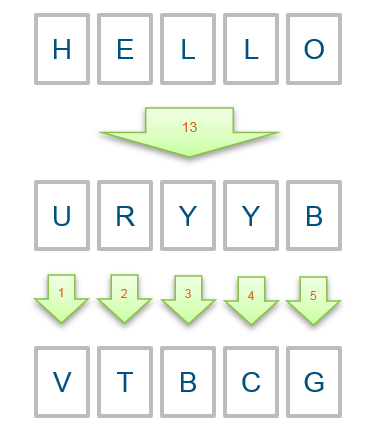
6.2.2 A example of cipher code of shift code 13
message = input("Enter a message to encode or decode: ") # Get a message
message = message.upper() # Make it all UPPERCASE :)
output = "" # Create an empty string to hold output
for letter in message: # Loop through each letter of the message
if letter.isupper(): # If the letter is in the alphabet (A-Z),
value = ord(letter) + 13 # shift the letter value up by 13,
letter = chr(value) # turn the value back into a letter,
if not letter.isupper(): # and check to see if we shifted too far
value -= 26 # If we did, wrap it back around Z->A
letter = chr(value) # by subtracting 26 from the letter value
output += letter # Add the letter to our output string
print("Output message: ", output) # Output our coded/decoded message
6.3 String Methods
6.3.1 Most user Python String Mehtod
- Get string Length
len()
s="a string"
print(len(s))
- Change case
s="Hello"
s.lower() # hello
s.upper() # HELLO
-
Sub String
s="Hello" s1=s[:2] # He s1=s[0:2] # He s2=s[3:] # lo s2=s[3:5] # lo s3=s[1:3] # el
6.3.2 Python String Cheat Sheet
https://www.shortcutfoo.com/app/dojos/python-strings/cheatsheet
6.4 Home work
6.4.1 Make you own ASCII Arts
- print it with the character in ASCII table
- Try to use number chr(n) to print
- Could use the examples in this class
- Charllenges
- Add color to your ASCII Arts
- Use array and loop to print your aSCII Arts
6.4.2 Make your double layer Cipher
Our cipher in the example is easy to cracked, make it harder to guess by double encode.
- Please write script to do the encode
- Please write another script decode your result of first result.